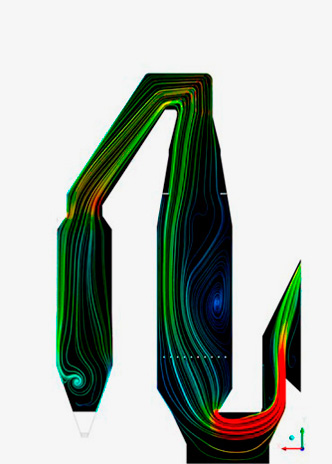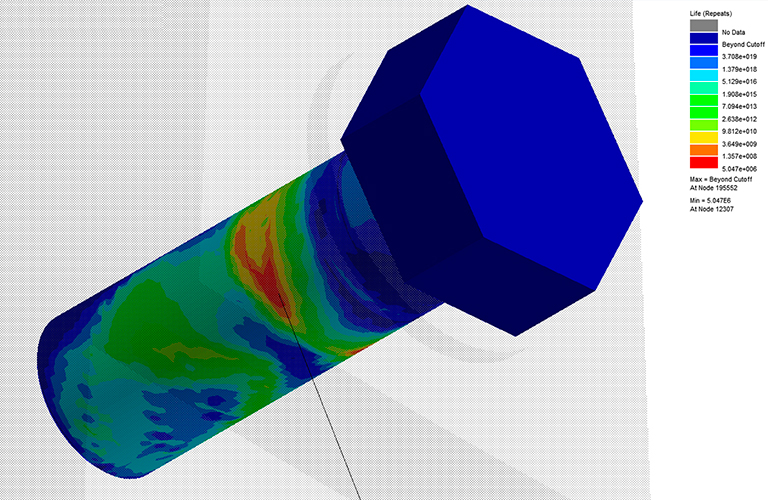
Simulation is a tool that uses mathematical models to represent physical phenomena through experimental or numeric computational techniques. It allows emulating reality to predict the operation of certain systems and anticipate problems.
In this way, it facilitates the task of identifying what type of responses may occur in given situations, preventing exposure to risk for people, equipment, structures, environment, etc.
- Simulation using the discrete element method (DEM).
- Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulation.
- Simulation by finite element method (FEM).
- Simulation of processes using continuous or discrete methods (Dynamic Simulation).
The Simulation of a Process Plant -both in the design stage and once active- allows the identification of important variables and parameters to increase the profitability of your project, since it actively collaborates in the resolution of problems, cost reduction, implementation of adjustments and validation of designs to maximize the efficiency and productivity of chemical, metallurgical and manufacturing plants. Through an exhaustive study of the production process, it is possible to identify and understand the main problems or opportunities for improvement associated with the operation or plant design, recognizing the critical variables and facilitating decision making.
The dynamic simulation of processes provides a representative prediction of the behavior of the critical operational variables of the processes, based on a thorough understanding of the physical and chemical phenomena involved. This, through the development of various mathematical models and with the substantial support of computational tools validated by the market.
The studies may focus on:
Predictive Study of Processes
If the plant design is in a pre-feasibility or feasibility stage, a Predictive Study of Processes can facilitate decision-making to obtain an optimal design that ensures the desired achievements in production, quality, and costs.
Process Optimization
If the plant is in an operational stage, the Process Optimization study can facilitate decision making that will lead to an improvement in its operational efficiency, reducing costs and supporting better management.
Through various studies of this discipline, the following can be obtained:
- Optimization of operational or design parameters.
- Capacity and storage analysis.
- Material handling analysis.
- Arrival logistics analysis (ships, trucks, cars, etc.).
- Dynamic mass, water, and energy balances.
- Analysis of plant performance against new technologies and designs.
- Identification of bottlenecks.
- Analysis and determination of plant availability and utilization.
- Identification of critical zones.
- Pulp and tailings transport study.
- Identification of training and qualification needs.

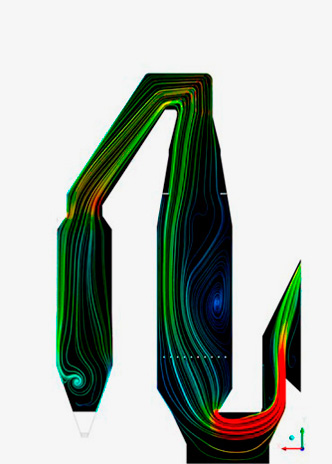
See more services:
Would you like to evaluate your project?
Let's talk!
+56 (2) 3224 3198
Download Brochure

Simulation is a tool that uses mathematical models to represent physical phenomena through experimental or numeric computational techniques. It allows emulating reality to predict the operation of certain systems and anticipate problems.
In this way, it facilitates the task of identifying what type of responses may occur in given situations, preventing exposure to risk for people, equipment, structures, environment, etc.
- Simulation using the discrete element method (DEM).
- Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulation.
- Simulation by finite element method (FEM).
- Simulation of processes using continuous or discrete methods (Dynamic Simulation).